1/3
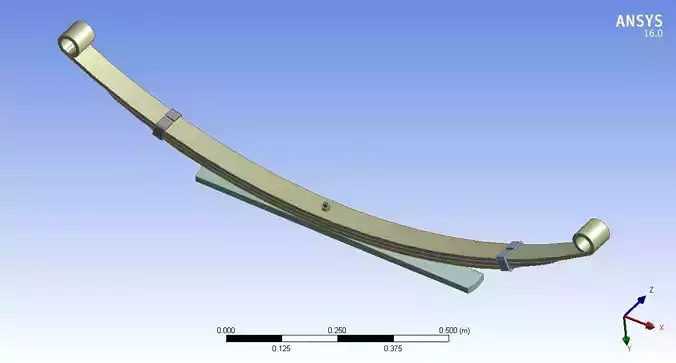
The design of leaf springs involves several key parameters that are carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and durability. These parameters include:
Material Selection:
Spring Steel: The primary material used for leaf springs due to its high tensile strength, toughness, and ability to withstand repeated bending without permanent deformation. Various grades of spring steel may be chosen based on the desired strength and flexibility characteristics.Dimensions:
Length: Determines the overall span of the leaf spring, which correlates with the wheelbase and chassis design of the vehicle.Width: Refers to the width of each individual leaf in the spring pack. Wider leaves generally offer greater load-carrying capacity.Thickness: The thickness of each leaf affects the spring's stiffness and load-carrying capacity. Thicker leaves are stiffer but may provide a rougher ride.Number of Leaves:
The number of leaves stacked together in the leaf spring pack influences its load-carrying capacity, flexibility, and resilience to fatigue. Multi-leaf springs distribute load more evenly and can provide smoother ride characteristics.Spring Rate:
The spring rate, or stiffness, of the leaf spring determines how much it deflects under a given load. It's influenced by factors such as the material properties, number of leaves, and dimensions of the leaves.Arch or Curve:
The arch or curvature of the leaf spring when unloaded affects its ability to flex and absorb shocks. The shape is designed to optimize load distribution and maintain proper wheel alignment under varying loads.End Configurations:
Spring Eyes: The ends of the leaf spring where it connects to the vehicle chassis and axle. These are typically designed with bushings or bushed bolts to allow controlled movement and reduce wear.Spring Shackles: Components that allow the leaf spring to pivot and change length as it flexes. Shackles are critical for maintaining proper suspension geometry and allowing for smooth articulation.Surface Finish and Protection:
Leaf springs are often treated with coatings or finishes to enhance corrosion resistance and durability. This includes processes like painting, galvanizing, or powder coating.Mounting and Attachment:
The method of attaching the leaf spring to the vehicle chassis and axle is crucial for ensuring stability, alignment, and load distribution. Proper mounting hardware and techniques are essential for safe operation.Load Capacity and Application:
The design parameters of leaf springs are tailored to the specific vehicle application, considering factors such as vehicle weight, payload capacity, intended use (on-road or off-road), and environmental conditions.Fatigue Resistance:
Leaf springs are subjected to cyclic loading and must be designed to withstand millions of cycles without failure. Factors such as material selection, surface treatments, and design configurations play a role in enhancing fatigue resistance.Overall, the design of leaf springs is a balance between stiffness, flexibility, durability, and weight, tailored to meet the specific requirements of the vehicle and its intended operating conditions. Advanced computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation tools are often used to optimize these parameters for performance and longevity.
REVIEWS & COMMENTS
accuracy, and usability.