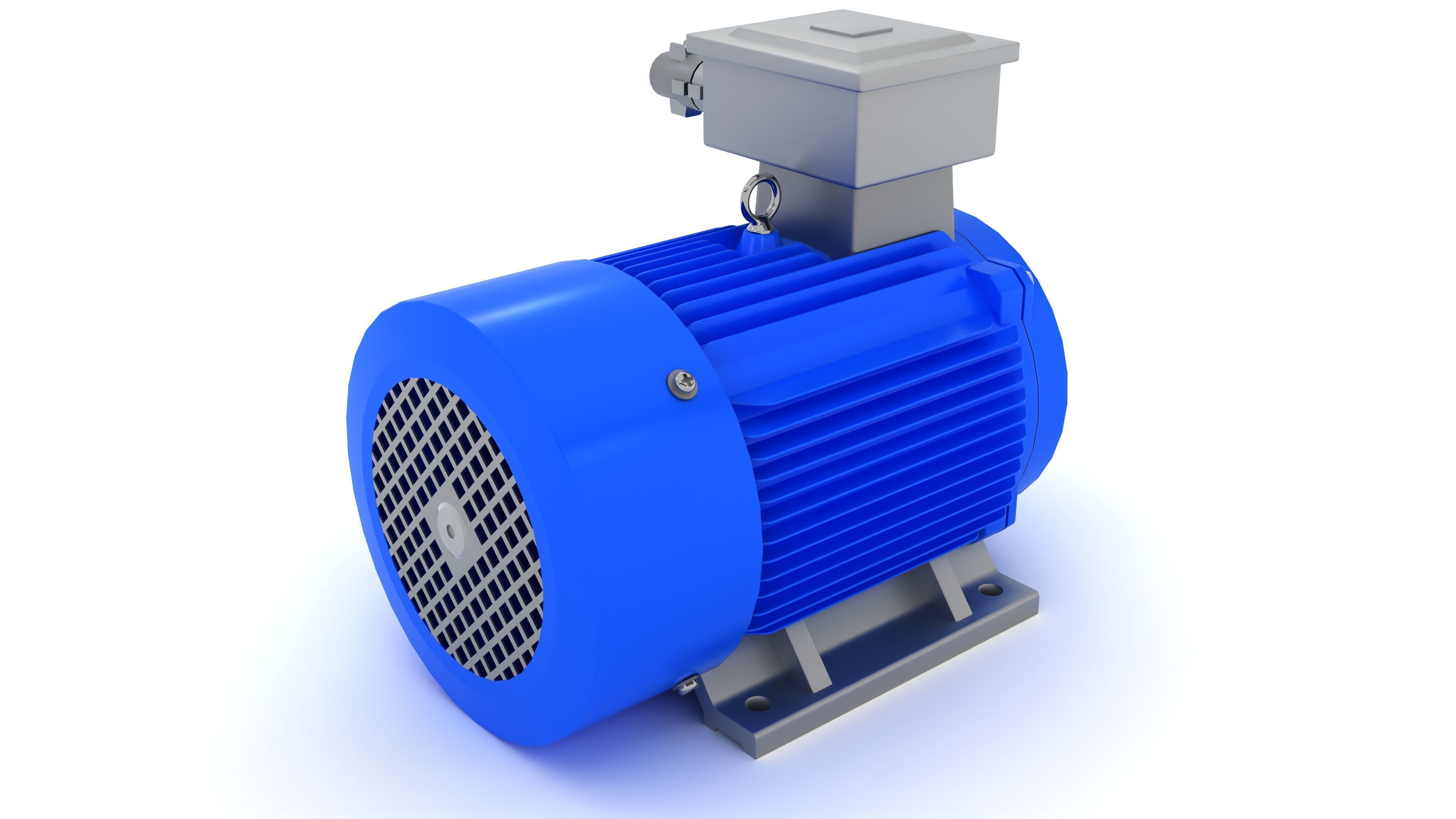
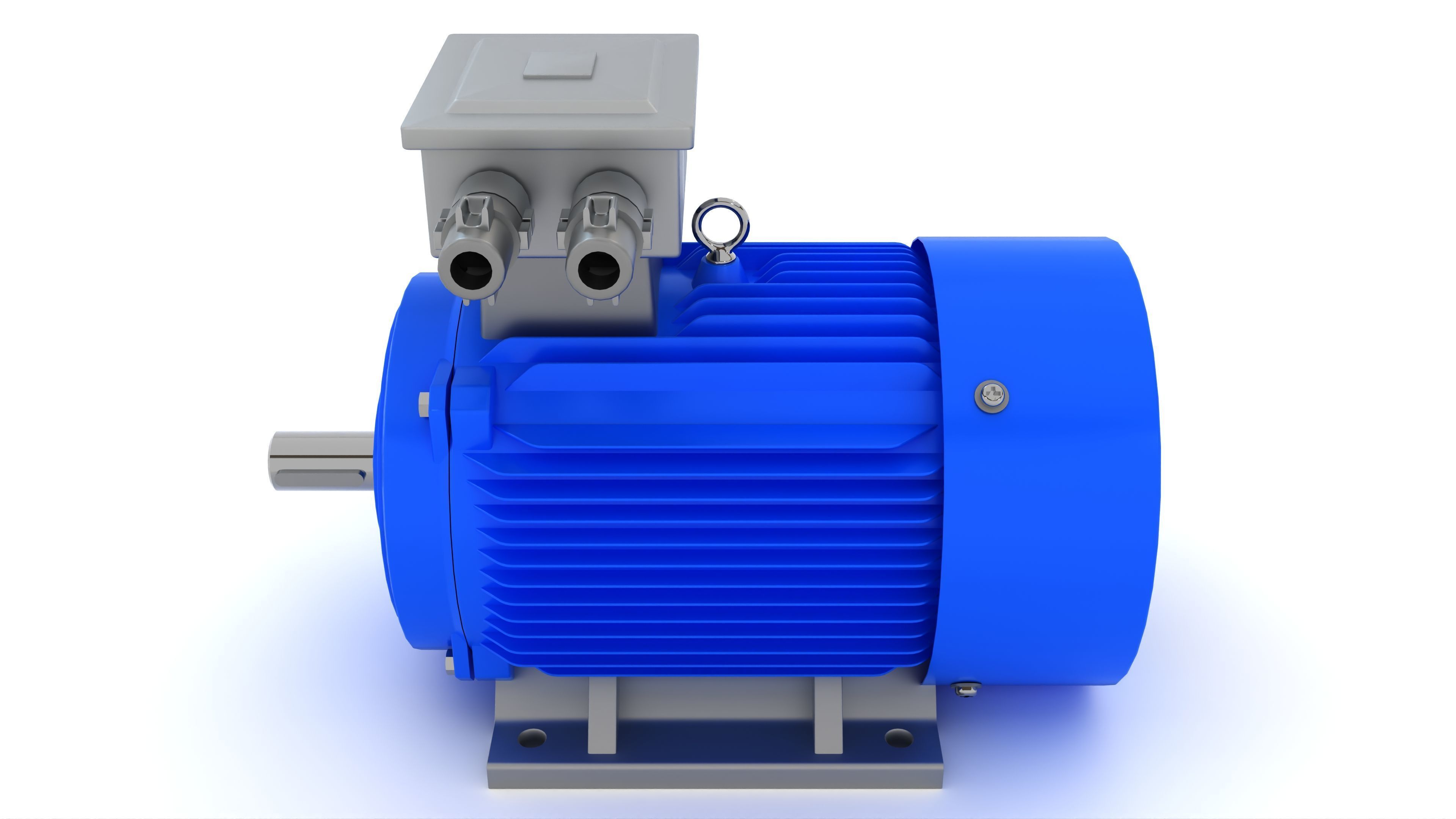
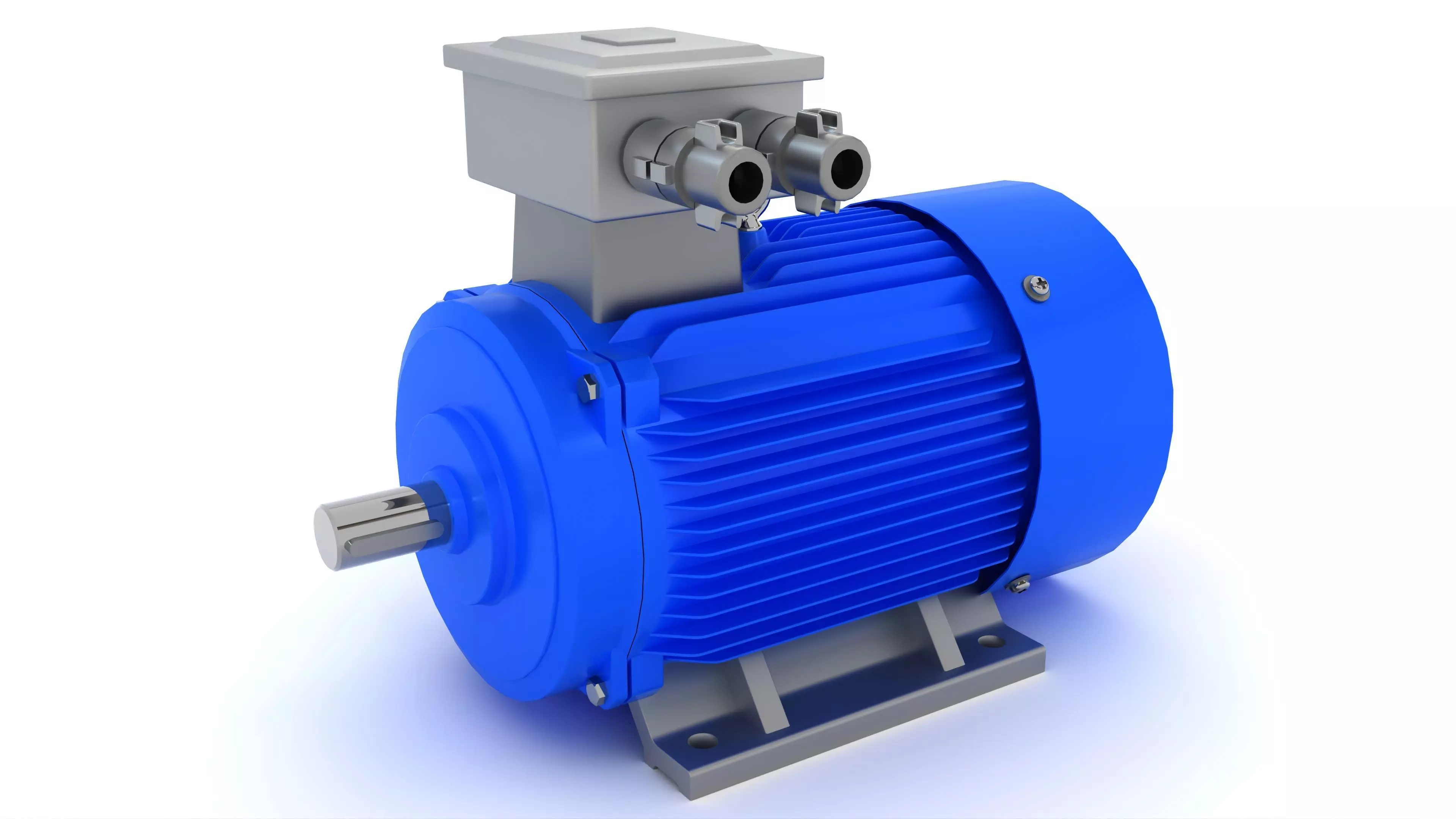
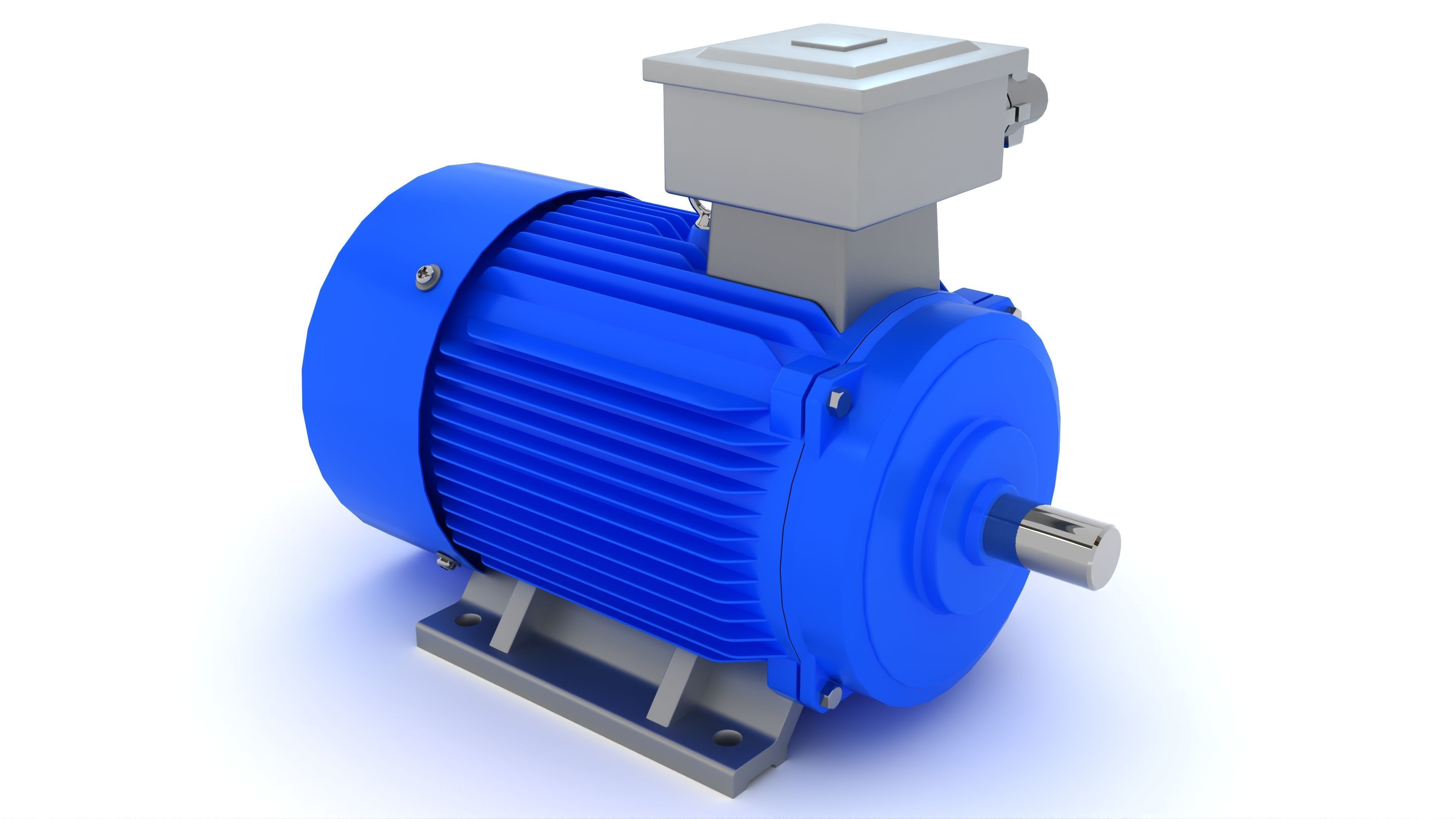
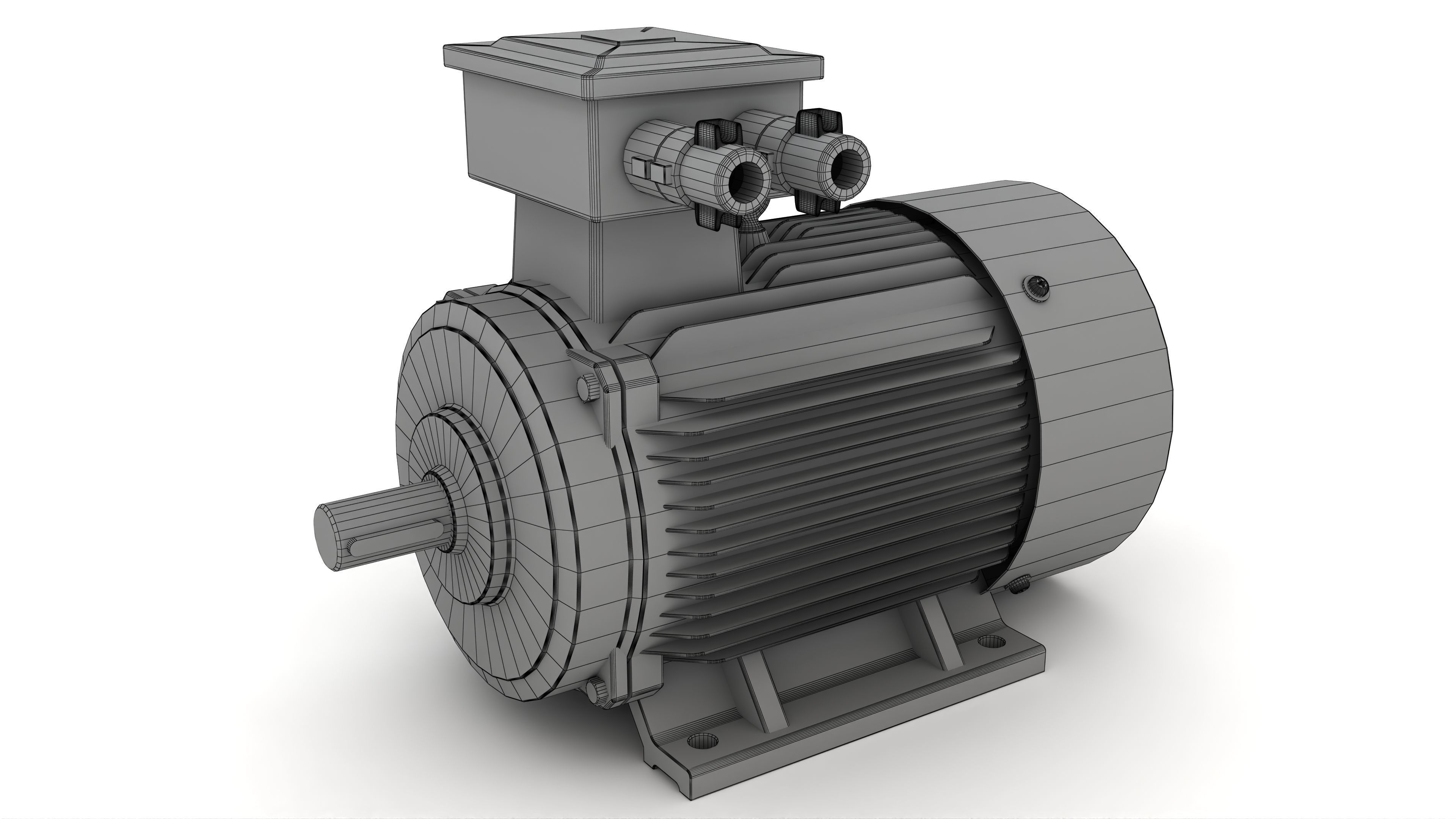
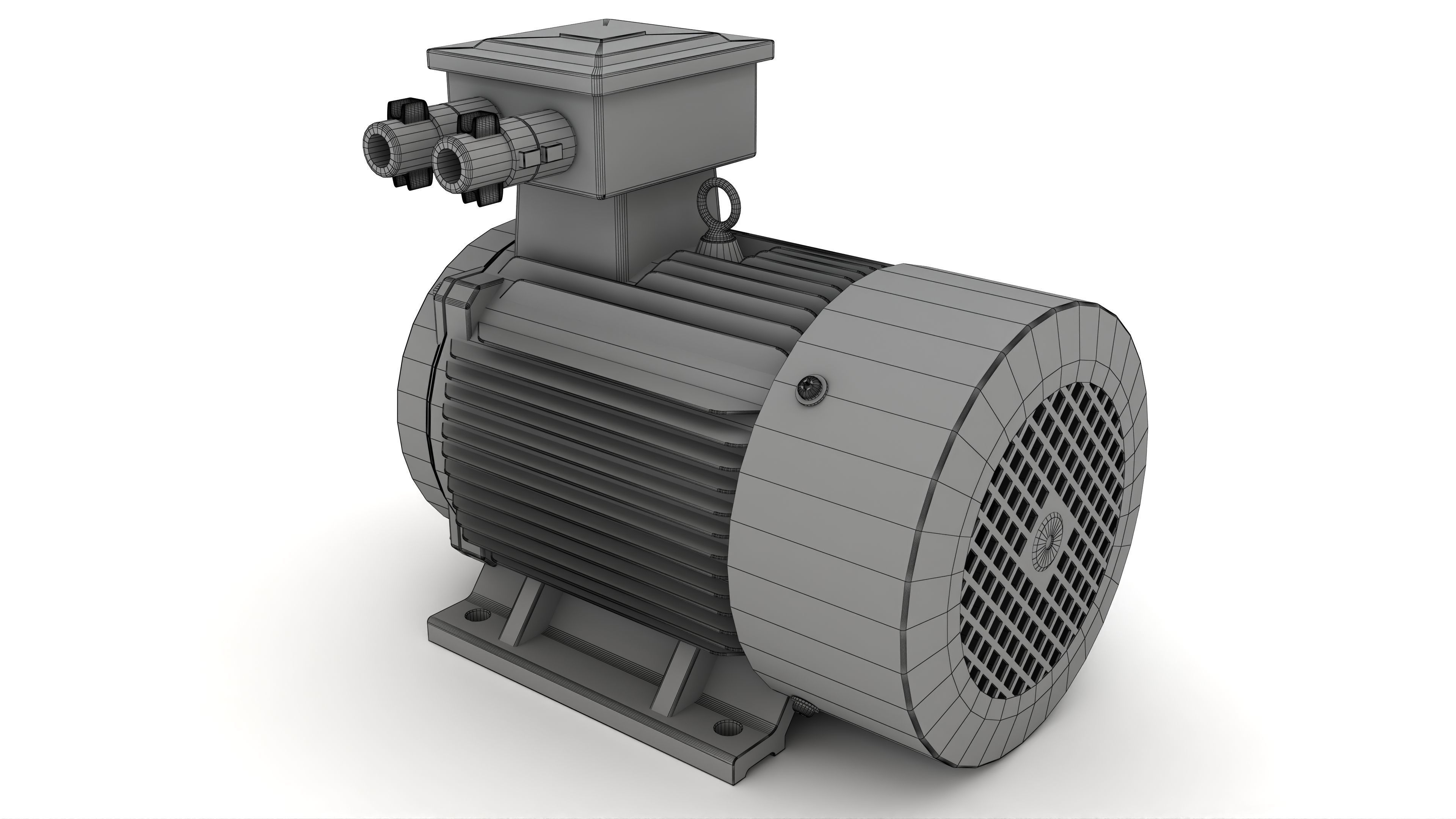
Electric Motor Generator 3D model
This Electric Motor Generator was modeled under 3Ds MAX 2020, the materials, Lighting and the rendering under V-Ray 7.
A Short History of the Electric Motor and GeneratorThe development of electric motors and generators traces back to the fundamental understanding of electromagnetism. Here’s an overview of their historical evolution:
Early Discoveries (1800s)1820s: Danish scientist Hans Christian Ørsted discovered the relationship between electricity and magnetism, laying the foundation for electromagnetism.1831: English scientist Michael Faraday demonstrated electromagnetic induction, showing that moving a conductor through a magnetic field generates electricity. This principle underpins the operation of both electric motors and generators.The Electric Generator1832: French instrument maker Hippolyte Pixii built the first dynamo (early generator), converting mechanical energy into electrical energy using Faraday’s principles.1867: German inventor Werner von Siemens improved the design with a self-exciting generator, eliminating the need for external magnets.The Electric Motor1828: Hungarian engineer Ányos Jedlik created one of the first known devices that converted electrical energy into motion using electromagnetism.1834: American inventor Thomas Davenport built the first practical electric motor, which could be used for industrial applications.Advancements in the Late 19th Century1873: Belgian engineer Zénobe Gramme developed a commercially viable generator that also functioned as a motor, demonstrating the reversible nature of these devices.1888: Serbian-American inventor Nikola Tesla patented the AC induction motor, which became the backbone of modern electric motors.The 20th Century and BeyondEarly 1900s: Development of more efficient motors and generators for industrial and household use, driven by advancements in materials and design.Mid-20th Century: Introduction of small, portable generators and specialized motors for consumer electronics and appliances.Late 20th Century to Present: Emergence of high-efficiency designs, such as brushless DC motors, and renewable-energy-based generators, like wind turbines and solar-powered systems.Today, electric motors and generators are integral to industries, transportation, and everyday life, embodying over two centuries of innovation in electromagnetism.