1/1
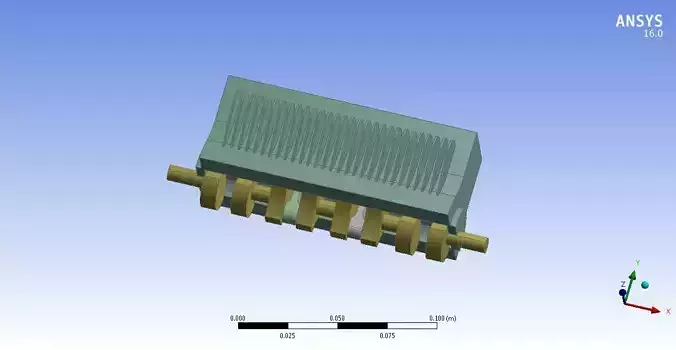
This CAD model is developed on Solidworks or Imported in Ansys workbench for analysis purpose. It is editable and easy to modify its features by using CAD Tools.
Key Features
Cylinder Block and Head:Cylinder Block: Houses the cylinders where combustion occurs. It contains passages for coolant and lubricating oil.Cylinder Head: Covers the top of the cylinder block, containing intake and exhaust ports, valves, and often the combustion chamber.
Pistons:Function: Move up and down within the cylinder to compress air-fuel mixture (in gasoline engines) or air (in diesel engines). Material: Typically made of aluminum alloy for light weight and thermal conductivity.
Connecting Rods:Function: Connect pistons to the crankshaft and convert reciprocating motion into rotational motion.Materials: Often made from steel, aluminum, or titanium depending on engine type and performance requirements.
Crankshaft:Function: Converts reciprocating motion of pistons into rotational motion to drive the vehicle. Material: High-strength steel, forged and machined to precise tolerances.
Valvetrain:Valves: Open and close to control intake of air (and fuel in gasoline engines) and exhaust of combustion gases. Camshaft: Rotates to open and close valves via cam lobes or through variable timing mechanisms (VVT).
Fuel System:Injection Systems: Deliver fuel into the combustion chamber at precise times and in precise amounts. Gasoline Engines: Use electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems. Diesel Engines: Use direct injection systems.
Ignition System:Spark Ignition: Uses spark plugs to ignite air-fuel mixture in gasoline engines. Compression Ignition: Relies on high compression temperatures to ignite air in diesel engines.
Cooling System:Function: Prevents engine overheating by circulating coolant through passages in the engine block and cylinder head. Components: Includes radiator, water pump, thermostat, and coolant passages.
Lubrication System:Function: Reduces friction between moving parts, dissipates heat, and carries away contaminants. Components: Oil pump, oil filter, and lubricating oil passages throughout the engine.
Exhaust System:Function: Guides and expels exhaust gases from the combustion chamber to the atmosphere. Components: Exhaust manifold, catalytic converter (for emissions control), and muffler.
Emission Control Systems:Catalytic Converter: Converts harmful gases (e.g., CO, NOx, hydrocarbons) into less harmful emissions. EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation): Reduces NOx emissions by recirculating a portion of exhaust gas into the intake manifold.
Engine Management Systems:ECU (Engine Control Unit): Controls and manages engine functions such as fuel injection timing, ignition timing, and emissions control. Sensors: Monitor various parameters (e.g., oxygen, temperature, pressure) to optimize engine performance and efficiency.
Power and Efficiency:Power Output: Measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW), reflects the engine's ability to perform work. Fuel Efficiency: Reflects the engine's ability to convert fuel energy into mechanical energy with minimal waste.
Durability and Maintenance:Materials: Engines use high-strength alloys and advanced manufacturing techniques for durability. Maintenance: Regular oil changes, filter replacements, and inspections to ensure longevity and performance.
Design Variants:Different Configurations: Engines vary in cylinder layout (inline, V-shaped, flat), displacement, and number of cylinders to suit different vehicle types and performance requirements.
REVIEWS & COMMENTS
accuracy, and usability.