1/13
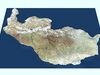
DescriptionNew Siberia Island. New Siberia or Novaya Sibir (/ˈnoʊvaɪə sɪˈbɪər/; Russian: Но́вая Сиби́рь, Nóvaya Sibír', [ˈnovəjə sʲɪˈbʲirʲ]; Yakut: Саҥа Сибиир, romanized: Saña Sibîr) is the easternmost of the Anzhu Islands, the northern subgroup of the New Siberian Islands lying between the Laptev Sea and East Siberian Sea. Its area of approximately 6,200 square kilometres (2,394 square miles) places it the 102nd largest islands in the world. New Siberia Island is low lying, rising to only 76 metres (249 feet) and covered with tundra vegetation. The island is a part of the territory of Russia's Sakha Republic. New Siberia Island consists of clastic sediments ranging from Late Cretaceous to Pleistocene in age. The Late Cretaceous sediments consist of extensively folded layers of gray and greenish gray tuffaceous sand, tuffaceous silt, pebbly sand, and layers of brown coal exposed in sea cliffs along it southwest coast. The sand and silt often contain either volcanic glass, fossil plants, rhyolite pebbles, or some combination of them. Eocene sand, silt, clay, and brown coal overlies an erosional unconformity cut into the Late Cretaceous sediments. Within the northwest part of New Siberia Island, these sediments grade into clays that contain fragments of marine bivalves. Directly overlying the Eocene sediments and another erosional unconformity are sands of Oligocene and Early Miocene age. They contain thin beds of silt, mud, clay, and pebbles. These sands contain fossil plants and lagoonal, swamp, and lacustrine diatoms. These sands are overlain by Pliocene sediments consisting of layers of sand, silt, mud, peat, and pebbles. Except for the Derevyannye Hills, Pleistocene sediments blanket almost the entire surface of New Siberia Island. These deposits consist of layers of marine sediments overlain by terrestrial sediments. The lower marine sediments are composed of three superimposed beds of marine to brackish water clay containing fossil mollusks and capped with peat. The overlying terrestrial sediments consist of an ice complex composed of ice-rich wind-blown silt in which ice wedges have developed. This ice complex accumulated over tens of thousands of years during the Late Pleistocene, through the Last Glacial Maximum, until it stopped at about 10,000 BP. During this period of tens of thousands of years, the formation of ice complex buried and preserved in permafrost an enormous number of mammoth tusks and bones and the bones of other “megafauna”. New Siberia Island is noted for abundant upright tree trunks, logs, leaf prints, and other plant debris that occur within sediments that are exposed along sea cliffs and within the uplands of the Derevyannye Hills along its southern coast. Due to the abundance of exposed coalified logs and upright trunks, early explorers and paleobotanists referred to the Derevyannye Hills as either the Wood Mountains, Wood Hills, or Tree Mountain. At one time, the highly folded layers of sand, silt, mud, clay, and brown coal containing these coalified tree fossils were once thought to have accumulated during either the Miocene or Eocene Epoch. These sediments and the fossil trunks and logs, which they contain, are now known to date to the Late Cretaceous Period (Turonian Stage). Baron Von Toll, Dr. Klubov and others, Dr. Dorofeev and others as well as other publications all demonstrate that the claims by some authors, i.e. Mr. Southall, that the Wood Hills of New Siberia Island are either partially or completely formed of driftwood are completely erroneous.
Texture Resolution: 640 x 454
REVIEWS & COMMENTS
accuracy, and usability.