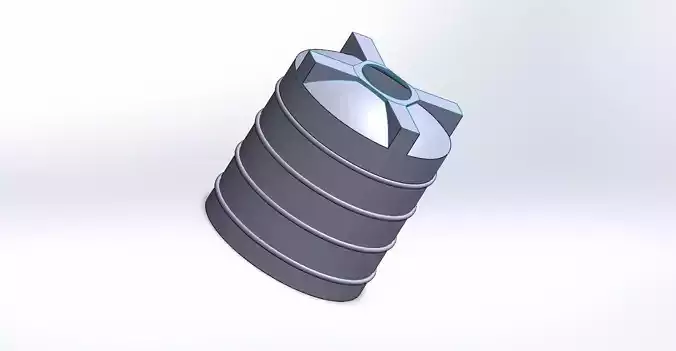
Designing a water tank involves considering several key factors to ensure it meets safety, durability, and usability requirements. Here’s a basic outline for designing a plastic water tank:
- Material SelectionChoose a suitable plastic material for the tank (e.g., polyethylene, fiberglass-reinforced plastic).Consider factors such as UV resistance, chemical resistance, and food-grade suitability.
- Capacity and DimensionsDetermine the required capacity of the tank based on the intended use (e.g., household, industrial).Calculate the dimensions (height, width, length) to accommodate the required capacity within the available space.
- Structural DesignDecide on the shape of the tank (e.g., cylindrical, rectangular) based on structural strength requirements and space constraints.Ensure the tank can withstand the weight of water and any additional loads (e.g., wind, seismic).
- Wall ThicknessCalculate the appropriate wall thickness considering the material properties, tank size, and intended usage.Factor in safety margins for maximum load conditions and long-term durability.
- ReinforcementsIncorporate reinforcements (ribs, supports) if needed to strengthen critical areas or to support additional equipment (e.g., pumps, valves).
- Inlet, Outlet, and FittingsDesign appropriate inlet and outlet openings considering flow rates and plumbing connections.Select fittings (valves, connectors) that are compatible with the tank material and ensure watertight seals.
- Accessories and FeaturesInclude features like inspection ports, overflow outlets, and level indicators as necessary.Ensure accessibility for maintenance and cleaning purposes.
- Testing and CertificationPerform structural and leakage tests to verify the design meets safety and performance standards.Obtain certifications (if required) for compliance with local regulations or industry standards.
- Manufacturing ConsiderationsConsult with manufacturers to optimize the design for production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.Consider factors such as mold design (for rotational molding or injection molding), batch sizes, and lead times.
- Installation and MaintenanceProvide guidelines for proper installation, including foundation requirements and securing methods.Specify maintenance procedures to ensure longevity and performance of the water tank.Regulatory ComplianceEnsure compliance with local building codes, health regulations, and environmental standards.Additional TipsDurability: Consider factors such as resistance to corrosion, temperature variations, and impact.Aesthetics: Balance functionality with aesthetic considerations if the tank will be visible.Lifecycle Cost: Evaluate the overall lifecycle cost including initial purchase, installation, maintenance, and replacement.By following these steps and considerations, you can design a plastic water tank that meets your specific requirements effectively and safely.