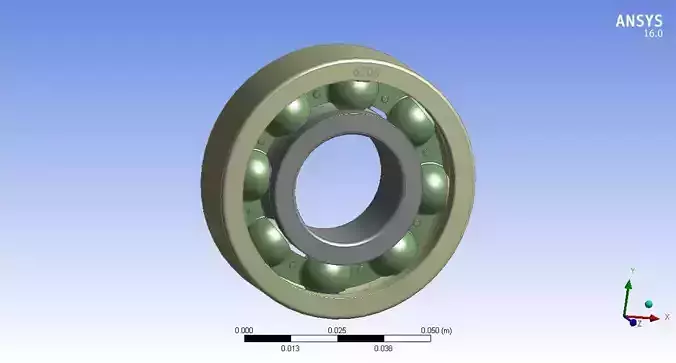
Designing ball bearings involves several critical considerations to ensure optimal performance, durability, and reliability in various mechanical applications. Ball bearings are essential components used to reduce friction between rotating parts by providing smooth rolling motion. Here are the key aspects involved in ball bearing design:
- Type of BearingRadial Ball Bearings: Designed to support radial loads (perpendicular to the shaft axis).Thrust Ball Bearings: Designed to support axial loads (parallel to the shaft axis).Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Designed to support combined radial and axial loads at specific angles.Deep Groove Ball Bearings: Designed for high-speed and radial load applications.
- Material SelectionInner and Outer Rings: Typically made from high-carbon chromium steel (e.g., AISI 52100) for strength, hardness, and wear resistance.Balls: Usually made from chrome steel, stainless steel, or ceramics. Material selection depends on factors such as load capacity, speed, corrosion resistance, and temperature.Cage (Retainer): Holds the balls in position and maintains equal spacing. Materials include brass, steel, nylon, or other polymers depending on the application requirements.
- Geometry and DimensionsRaceway Profiles: Inner and outer raceways are typically designed with a groove or track to guide the balls.Ball Diameter: Determines load-carrying capacity and contact angle.Clearance: Radial and axial clearance between components to accommodate thermal expansion and ensure smooth operation.Preload: Axial or radial load applied to the bearing during assembly to reduce internal clearance and minimize play.
- LubricationGrease vs. Oil: Selection of lubricant based on operating speed, temperature, and environmental conditions.Seals and Shields: Protect bearings from contaminants and retain lubrication. Options include rubber seals, metal shields, or open designs.Lubrication Interval: Determine the frequency of lubrication based on operating conditions and bearing type (e.g., high-speed bearings may require continuous lubrication).
- Load and Speed RatingsDynamic Load Rating: Maximum load that a bearing can withstand for a specified number of revolutions before fatigue failure.Static Load Rating: Maximum load that a bearing can withstand without permanent deformation.Limiting Speed: Maximum rotational speed at which a bearing can operate without excessive heat generation and premature failure.
- Mounting and InstallationFit Tolerances: Ensure proper fit between shaft and housing to prevent misalignment and excessive load on the bearing.Mounting Methods: Press fit, shrink fit, or interference fit depending on bearing size and application.Alignment: Proper alignment of shaft and housing to minimize stress and ensure smooth operation.
- Testing and Quality ControlDimensional Accuracy: Verify critical dimensions such as bore diameter, outer diameter, and raceway profile.Surface Finish: Ensure smooth and precise surfaces to reduce friction and wear.Noise and Vibration Testing: Assess bearing performance under operational conditions to detect abnormalities or defects.
- Environmental ConsiderationsCorrosion Resistance: Select materials and coatings to withstand exposure to moisture, chemicals, and other environmental factors.Temperature Range: Design bearings to operate within specified temperature ranges without loss of performance.
- Advanced Design ToolsCAD Software: Use tools like SolidWorks, AutoCAD, or specialized bearing design software to model and simulate bearing performance.Finite Element Analysis (FEA): Analyze stress distribution, deformation, and thermal effects to optimize bearing design.In summary, ball bearing design requires careful consideration of materials, geometry, lubrication, load ratings, and environmental factors to ensure reliable and efficient performance in diverse industrial applications. Advanced design tools and testing methods play a crucial role in optimizing bearing design for specific operating conditions and durability requirements.