Useto navigate. Pressescto quit
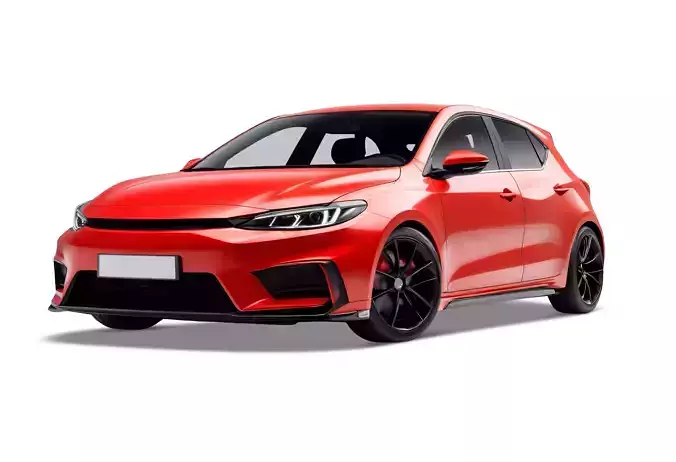
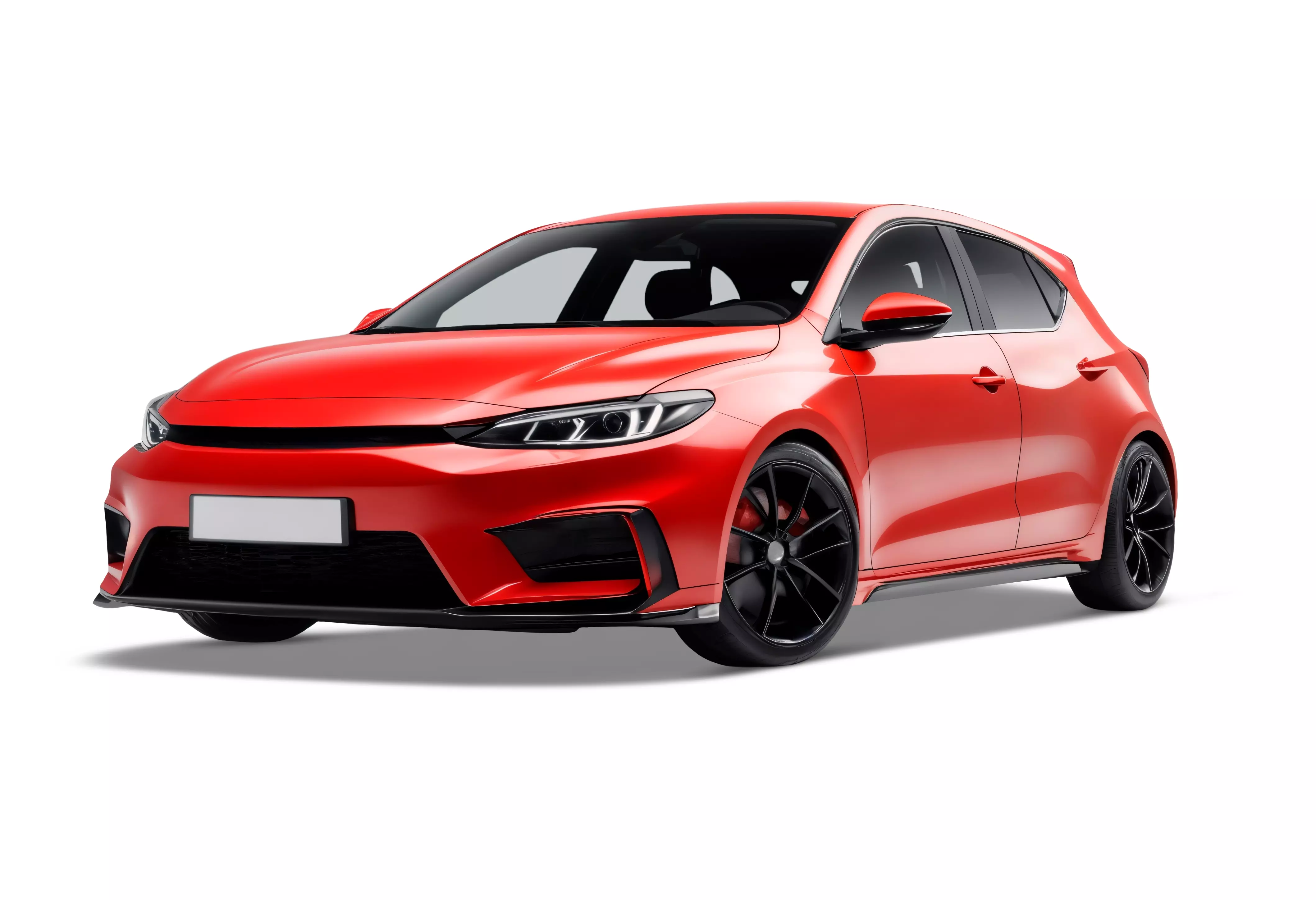
3d Red Premium Car 3D model
Verification details of the FBX file
Files
Binary FBX
Scene
No unsupported objects
Geometry
No N-gonsNo faceted geometryManifold geometry
Textures and Materials
PBR texturesNo embed texturesSquare texturesPower of 2 texture sizesAssigned materials
UVs
No UV overlapsUV unwrapped model
Naming
Allowed characters
Description
3D car modeling refers to the process of creating a digital representation of a car using 3D modeling software. This is commonly done in industries such as automotive design, gaming, animation, and simulation. The process involves several stages, from conceptualization to final rendering. Here's an outline of the typical steps involved:
- Conceptualization & ResearchBefore creating a 3D model, a clear understanding of the car's design is required. This might involve gathering references like blueprints, photos, or design sketches.The designer considers the car's overall shape, size, features, and how it will be used (e.g., a sports car, SUV, etc.).
- Modeling the Car's GeometryThe primary step in 3D car modeling is constructing the car's basic structure. The model is typically created in wireframe form.Polygonal modeling is often used, where the car's shape is built from polygons (usually quads or triangles). Artists begin by creating the main body, followed by other parts like wheels, windows, mirrors, etc.NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) might also be used for smoother, curved surfaces. This is often preferred for designing vehicles, as it allows for precise control over curves and shapes.
- DetailingOnce the rough model is complete, finer details are added. These details might include headlights, taillights, grills, door handles, vents, and other small elements that make the car look realistic.At this stage, modeling software tools like subdivision surfaces (SubD) might be used to smooth out the model and add more detail.
- UV MappingUV Mapping is the process of unwrapping the 3D model to create a 2D representation of its surface. This allows textures and materials to be applied correctly to the model.A good UV map ensures that textures (such as paint, metal, glass, etc.) are applied in a way that aligns with the real-world surface of the car.
- TexturingTextures are applied to give the car surface realistic materials. For instance, the car body might have a reflective paint texture, while the tires might use a rubber texture.High-quality textures can include details like dirt, scratches, or wear-and-tear effects to make the car look more realistic.
- Shading and MaterialsIn this stage, shaders and materials are applied to give realistic appearances to different surfaces of the car.Shaders control the way light interacts with the model, making it look glossy, matte, transparent, or metallic.Materials like glass, rubber, and metal have specific properties that must be accurately replicated for realism.
- Lighting & RenderingLighting is essential for bringing the model to life. The 3D model can be rendered in various ways depending on its intended use—whether it's for a game engine, a film, or an advertisement.Rendering is the process of generating the final image or animation from the 3D scene, including the car model, lights, textures, and camera settings. Software like V-Ray, Arnold, or Blender's Cycles is often used to generate photorealistic renders.
- Animation (Optional)If the 3D model is being used for animation (e.g., a car chase scene in a movie), rigging and animation are the next steps.Rigging involves setting up the skeleton and control systems for the car, while animation involves creating movements like the car driving, doors opening, or wheels rotating.
- Post-Processing (Optional)After rendering the final image or animation, additional effects or touch-ups can be done in post-processing software like Photoshop or After Effects.This can include adding motion blur, reflections, or other visual effects to enhance realism.Tools Used for 3D Car Modeling:Blender: A popular, open-source 3D modeling and rendering software.Autodesk Maya: Commonly used for animation and modeling, known for its versatility and powerful tools.Autodesk 3ds Max: Used for modeling and rendering, especially in automotive design.Cinema 4D: Known for its user-friendly interface and motion graphics capabilities.Rhinoceros (Rhino): Often used for more precise, NURBS-based modeling in automotive design.Applications of 3D Car Modeling:Automotive Design: Manufacturers use 3D modeling to design cars before physical prototypes are made.Video Games: Cars are modeled and animated for use in racing games and open-world games.Animation & Movies: 3D cars are often used in CGI-heavy movies and TV shows.Virtual Reality (VR): Cars can be modeled for simulation or VR experiences, like test-driving in a virtual environment.3D car modeling is a complex and creative process, requiring a deep understanding of both design principles and 3D software tools to create realistic, functional car models.