1/12
Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assisting in the removal of metabolic wastes.[2] In humans, the heart is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest.[3]
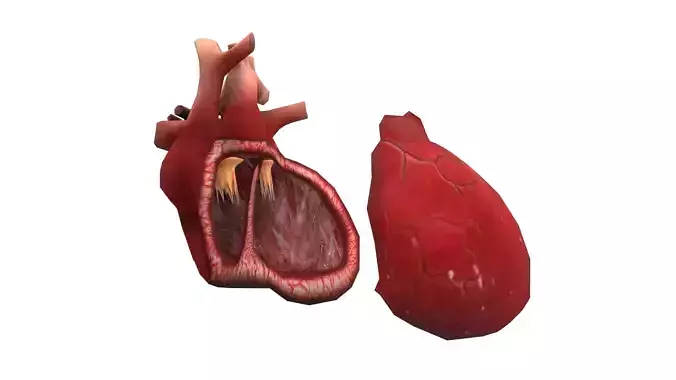
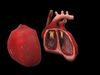
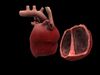
In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria; and lower left and right ventricles.[4][5] Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart.[6] Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while reptiles have three chambers.[5] In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow.[3] The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of the heart is made up of three layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.[7]
The heart pumps blood with a rhythm determined by a group of pacemaking cells in the sinoatrial node. These generate a current that causes contraction of the heart, traveling through the atrioventricular node and along the conduction system of the heart. The heart receives blood low in oxygen from the systemic circulation, which enters the right atrium from the superior and inferior venae cavae and passes to the right ventricle. From here it is pumped into the pulmonary circulation, through the lungs where it receives oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium, passes through the left ventricle and is pumped out through the aorta to the systemic circulation−where the oxygen is used and metabolized to carbon dioxide.[8] The heart beats at a resting rate close to 72 beats per minute.[9] Exercise temporarily increases the rate, but lowers resting heart rate in the long term, and is good for heart health.
REVIEWS & COMMENTS
accuracy, and usability.