1/6
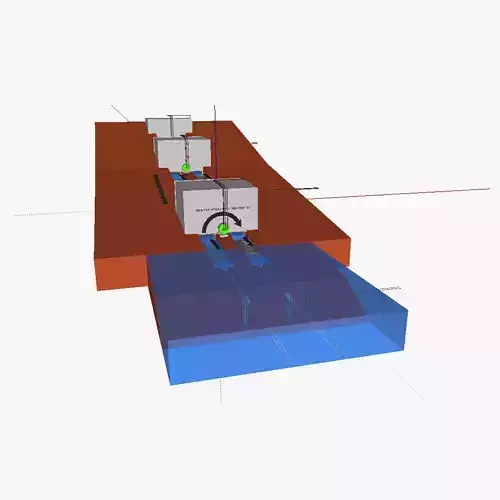
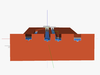
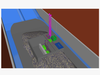
3D model of the water-based freight transport system (WFTS). The water-based freight transport system is a system that transports freight using boats that do not have their own propulsion system. The boats (actually barges) are instead propelled using gravity (which is similar as how it is done with the Stevelduct ) on downwards canal sections, and using a Hallidie cable car system on slight upward slopes and flat canals. The Eppelsheimer bottom cable car gripper is used on the boats to grab the cable, which is circulated using a motorized roller. For major upward slopes, a variant of the Stevelduct's revolving elevator can also be used. This elevator is rather energy-efficient, as per rotation, 2 boats are loaded in opposing sides, leveling out the weight. The motor than rotates drum, moving up one boat and lowering another. It should be noted that the a canals are 1-way direction. Besides the cable gripper, there is also a rail gripper on the boat; this serves to keep the boat steady and perfectly straight. Both the cable gripper and the rail gripper can be moved upwards or downwards by gripper motor 1 and 2 -G1M and G2M- ; this allows the boat to follow a right or left bend within the canals. As such, the boat can travel to many destinations, rather than just 1 destination as with the Stevelduct.
Next, an explaination on how the onboard system exactly works: RFID antenna 2 serves to receive RFID signals from the gates with passive RFID, and from other barges. The barges continuously sent RFID signals using RFID antenna 1; when they approach a gate with passive RFID, the RFID signal is returned in a specific way. This tells the barge not only that it has arrived at an intersection, but also where he is (at which gate) along his trajectory. The PCB then searches on his on-board memory which turn he has to take (left or right) and then takes the correct turn by either connecting/disconnecting the cable gripper and lowering/heightening the rail gripper. The PCB is powered by the battery which is itself recharged using a solar panel, small windturbine or other power plant.
When the barges come too close to each other (and when there is thus a risk of collision), RFID antenna 2 detects the transmissions of RFID antenna 1 of the other barge. The PCB then orders to disconnect the Eppelsheimer gripper from the cable, slowing down and ultimately halt the vessel.
REVIEWS & COMMENTS
accuracy, and usability.