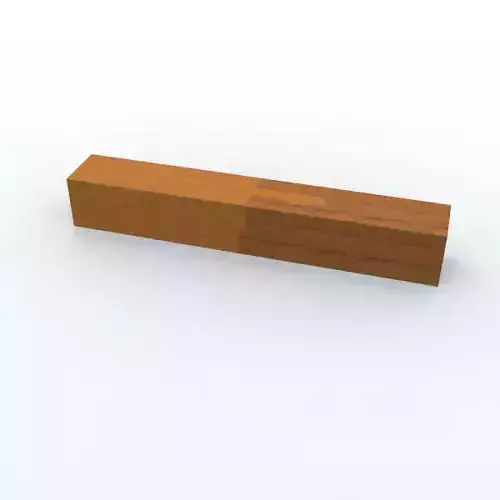
3D Features
Animated
The model includes animations (movement or actions) that can be played in supported software or engines.
Rigged
The model has a skeleton or bone structure, making it ready for posing or animation.
Low-poly
PBR
Uses Physically Based Rendering materials, which give the model realistic lighting and surface properties.
Textures
The model includes image files (textures) that add color, patterns, or detail to its surfaces.
Materials
The model has material settings that define how surfaces look (color, shine, transparency, etc.).
UV Mapping
The model's surfaces are mapped to a 2D image, allowing textures to display correctly.
Plugins Used
Some external plugins were used to create the model. These may be required for full functionality.
3D printing
Indicates whether the designer marked this model as suitable for 3D printing.
Model is not 3D printable
The designer indicates this model is intended for digital use only (rendering, animation, or AR/VR) and not for 3D printing.
Geometry
465 polygons
The total number of polygons (flat shapes) that make up the 3D model.
/ 594 verticesThe number of points (corners) that define the shape of the model's polygons.
Unwrapped UVs
Unknown
Publish date
2023-09-16
Model ID
#4779796